Project successfully tests feasibility of lithography-based metal Additive Manufacturing for lunar environment
July 12, 2023
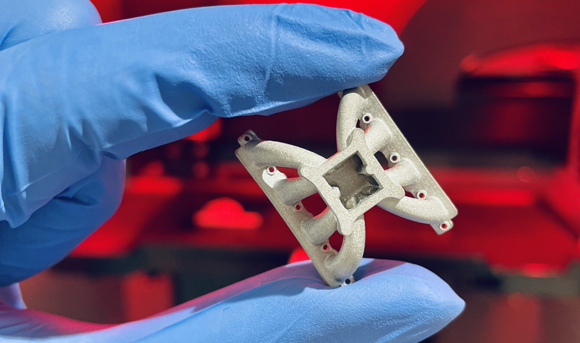
roject with the European Space Agency (ESA), OHB System AG, in Bremen, Germany, and Lithoz GmbH, Vienna, Austria, to test the potential of Additive Manufacturing and a zero-waste workflow for the lunar environment. The ESA-sponsored project, undertaken by Incus and Lithoz GmbH under the coordination of OHB System AG as prime contractor, aimed to research the feasibility of processing lunar scrap, which might be recovered from debris from old missions or satellites, to produce high-quality parts using Additive Manufacturing, which could help and enhance human settlement on the Moon.
The successful use of lunar resources and recycling of scrap metals is vital to the creation of a sustainable Moon base. Lithography-based metal manufacturing was reportedly selected for its ability to use recycled metal waste and its ease and safety during the build and post-processing stages. The lithography-based metal manufacturing (LMM) technology, defined as a vat photopolymerisation process (VPP) by ISO/ASTM, is a process which is said to produce parts with similar material properties found in Metal Injection Moulding (MIM).
The greatest challenge for lunar Additive Manufacturing is the harsh lunar environment, including the atmosphere, gravity, temperature, radiation, and the potential contamination of moon dust. Despite these challenges, the Incus Hammer Lab35 Additive Manufacturing machine was reportedly able to produce parts demonstrating a high level of strength, comparable to MIM titanium parts standards (1000-1050 MPa).
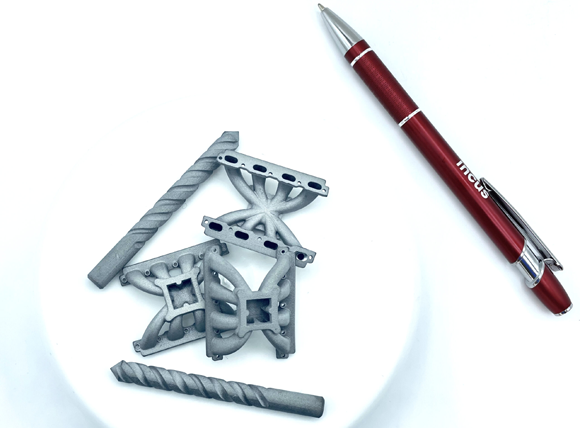

Without the need for any support structures, the LMM process offered a sustainable zero-waste workflow. The project also included the development of a green binder and the optimisation of pre-and post-processing steps to build and test different demonstrators for future lunar applications.
“This project has proven that LMM technology is able to use recycled powder for the feedstock material and provide sustainable zero-waste workflow,” stated Incus CEO, Dr Gerald Mitteramskogler. “We expect that further developments in metal recycling technologies will open the way to metal materials with more settled sintering processes for the lunar environment.”
The project’s optimal scenario for the Additive Manufacturing habitat on the Moon base is reportedly comparable to that on Earth, with reduced gravity and human-graded radiation shielding, ensuring that no major modifications or redesigns are required aside from the size, mass and volume reduction of the Additive Manufacturing machine.

“Considering the challenge of bringing humans back to the Moon and building a base, the topic of in-situ resource utilisation (ISRU) is gaining significant momentum. Projects like this, recently completed by Incus and project partners, demonstrate that manufacturing methods like LMM are very good candidates to support such an endeavour,” added Dr Martina Meisnar, Materials and Processes Engineer at ESA.
“This successful collaboration showed that lithography-based AM techniques are among the most promising candidates to let 3D printing in space become a reality in the future,” concluded Dr Martin Schwentenwein, Head of Material Development at Lithoz.
Download PIM International magazine


















