An in-vivo study of MIM 316L bone fracture fixation plates
December 2, 2015
MIM is regarded as offering a revolutionary new class of medical implants for orthopaedics. Dr Mohd Afian Omar and his colleagues at the Advanced Materials Research Center (AMREC), SIRIM Berhad and Faculty of Medicine, International Islamic University of Malaysia (IIUM), have been investigating the in-vivo study of MIM 316L stainless steel fracture fixation plates for bone fracture repair.
In order to evaluate the bone tissue reaction to the 316L stainless steel plates manufactured by MIM for in bone plate fixation, an experiment with rabbits was performed by a group of orthopaedic surgeons and researchers from the Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, IIUM and Biomedical Materials Programme, AMREC. This is the continuation of successful collaboration research between SIRIM Berhad and IIUM for the fabrication of injection moulded fracture fixation plates over the last two years. In this study, the animal experiments on fracture fixation were investigated by radiographic assessment and gross inspection via hard tissue processing, since each sample comprises bone and metal plate. A total of 40 rabbits were used for this study. Experimental fractures were made in rabbit tibia and fixed with either a MIM plate or a conventional mini plate which served as a control.
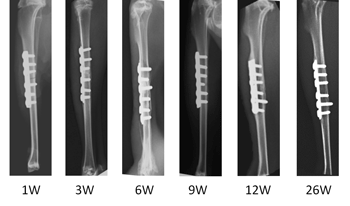
In X-Ray assessment at the three week interval post-surgery, bridging callus is present in both groups (Fig. 1). The bone union was obtained and the fracture line invisible at week six. Early intramedullary canal is taking place at week nine and at week twelve, continuity of bone cortex is present. The new bone is fully remodelled and the plate in-situ in both groups at week 26. For gross inspection, at week three of post implantation (Fig. 2a) no obvious changes occurred, the transverse fracture at mid shaft tibia was noted with implant in-situ. Fracture callus was present but was immature and soft. The new bone had covered the plate and strongly bonded to the surface of the plate at week 26 (Fig. 2b) and the plate is straight and parallel to the operated bone.
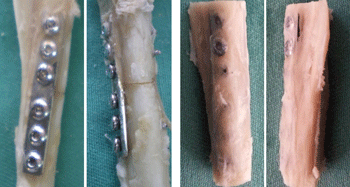
Fig. 2 Implantation of MIM plates at different weeks: a) MIM plate at week 3, b) MIM plate at week 26
Callus formation was seen along the implantation site in MIM plates. The fracture was healed after application of MIM plate without any soft tissue reaction. Thus, results of the present study show the return of the bone to normal anatomy is achieved with the presence of bone remodeling at week 12. This showed that the MIM plate is able to sustain its function from day one of fixation until remodeling take place at week 26.
Data from radiographic analysis and gross observation evidenced that MIM plates are compatible and able to induce new bone formation. These results revealed that the MIM plate shown has the comparable function capabilities as the conventional plate to hold the fracture fragments and promote immobilisation for the fracture healing process. Therefore, the MIM plates can be used as an alternative internal fixator for fracture management in orthopaedics.
Email: [email protected] | www.sirim.my